

Monthly Report on Credit and Liquidity Programs
and the Balance Sheet
| Lending Facilities | Lending in Support of Specific Institutions | Financial Tables |
Lending in Support of Specific Institutions
Quarterly Developments
- Cash flows generated from the Maiden Lane II LLC and Maiden Lane III LLC portfolios are used to pay down the Federal Reserve Bank of New York's (FRBNY's) loans to those LLCs. For the second quarter of 2010, repayments totaled approximately $2 billion, as presented in tables 18 and 21.
Background
During the financial crisis, the Federal Reserve extended credit to certain specific institutions in order to avert disorderly failures that could result in severe dislocations and strains for the financial system as a whole and harm the U.S. economy. In certain other cases, the Federal Reserve committed to extend credit, if necessary, to support important financial firms.
Bear Stearns and Maiden Lane LLC
In March 2008, the FRBNY and JPMorgan Chase & Co. (JPMC) entered into an arrangement related to financing provided by the FRBNY to facilitate the merger of JPMC and The Bear Stearns Companies Inc. (Bear Stearns). In connection with the transaction, the Federal Reserve Board authorized the FRBNY, under Section 13(3) of the Federal Reserve Act, to extend credit to a Delaware limited liability company, Maiden Lane LLC, to partially fund the purchase of a portfolio of mortgage-related securities, residential and commercial mortgage loans, and associated hedges from Bear Stearns. In the second quarter of 2008, the FRBNY extended credit to Maiden Lane LLC. The LLC manages its assets through time to maximize the repayment of credit extended to the LLC and to minimize disruption to the financial markets.
Table 13. Fair Value Asset Coverage
Millions of dollars
| Fair value asset coverage of FRBNY loan on 6/30/2010 | Fair value asset coverage of FRBNY loan 3/31/2010 | |
|---|---|---|
| Maiden Lane LLC | (17) | (1,255) |
| Maiden Lane II LLC | 1,652 | 915 |
| Maiden Lane III LLC | 7,453 | 6,374 |
The two-year accumulation period that followed the closing date for Maiden Lane LLC ended on June 26, 2010. Consistent with the terms of the Maiden Lane LLC transaction, the distribution of the proceeds realized on the asset portfolio held by Maiden Lane LLC, after payment of certain fees and expenses, will occur on a monthly basis going forward unless otherwise directed by the Federal Reserve. The monthly distributions will be used to cover the expenses and repay the obligations of the LLC, including the principal and interest on the loan from the FRBNY.
The assets of Maiden Lane LLC are presented weekly in tables 1, 10, and 11 of the H.4.1 statistical release. Additional details on the accounts of Maiden Lane LLC are presented in table 4 of the H.4.1 statistical release. Details of the terms of the loan, as well as information on the holdings of the Maiden Lane LLC, including the CUSIP number, descriptor, and the current principal balance or notional amount outstanding for nearly all of the holdings of Maiden Lane LLC with the exception of residential whole loans, is published on the FRBNY website at www.newyorkfed.org/markets/maidenlane.html.
Information about the assets and liabilities of Maiden Lane LLC is presented as of June 30, 2010, in tables 14 through 16 and figure 2. This information is updated on a quarterly basis.
Table 14. Maiden Lane LLC Outstanding Principal Balance of Loans
Millions of dollars
| FRBNY senior loan | JPMC subordinate loan | |
|---|---|---|
| Principal balance at closing | 28,820 | 1,150 |
| Most Recent Quarterly Activity | ||
| Principal balance on 3/31/2010 (including accrued and capitalized interest) | 29,276 | 1,264 |
| Accrued and capitalized interest 3/31/2010 to 6/30/2010 | 55 | 17 |
| Repayment during the period from 3/31/2010 to 6/30/2010 | _ | _ |
| Principal balance on 6/30/2010 (including accrued and capitalized interest) | 29,331 | 1,280 |
Table 15. Maiden Lane LLC Summary of Portfolio Composition, Cash and Cash Equivalents, and Other Assets and Liabilities
Millions of dollars
| Fair value on 6/30/2010 | Fair value on 3/31/2010 | |
|---|---|---|
| Federal Agency and GSE MBS | 19,880 | 18,794 |
| Non-agency RMBS | 1,922 | 1,936 |
| Commercial loans | 4,823 | 4,464 |
| Residential loans | 611 | 604 |
| Swap contracts1 | 958 | 903 |
| Other investments | 1,029 | 969 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | 1,299 | 1,229 |
| Other assets2 | 463 | 297 |
| Other liabilities1,3 | (1,671) | (1,173) |
| Net assets | 29,314 | 28,022 |
1. Fair value of swap contracts is presented net of associated liabilities. Return to table
2. Including interest and principal receivable and other assets. Return to table
3. Including amounts payable for securities purchased, collateral posted to Maiden Lane LLC by swap counterparties, and other liabilities and accrued expenses Return to table
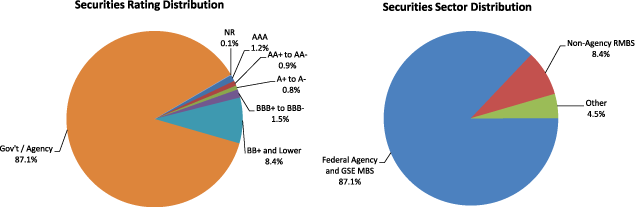
Table 16. Maiden Lane LLC Securities Distribution by Sector and Rating
Percent, as of June 30, 2010
| Sector1 | Rating | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAA | AA+ to AA- | A+ to A- | BBB+ to BBB- | BB+ and lower |
Gov't/ Agency |
Not rated | Total | |
| Federal Agency and GSE MBS | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 87.1 | 0.0 | 87.1 |
| Non-agency RMBS | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 7.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 8.4 |
| Other2 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 4.5 |
| Total | 1.2 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 8.4 | 87.1 | 0.1 | 100.0 |
1. Does not include Maiden Lane LLC's swaps and other derivative contracts and commercial and residential mortgage loans. Return to table
2. Includes all asset sectors that, individually, represent less than 5 percent of the aggregate fair value of securities in the portfolio. Return to table
Figure 2. Maiden Lane LLC Securities Distribution as of June 30, 2010
American International Group, Inc. (AIG)
Recent Developments
- On September 30, 2010, AIG announced an agreement with the U.S. Department of the Treasury, the Federal Reserve Bank of New York (FRBNY), and the trustees of the AIG Credit Facility Trust on a comprehensive recapitalization plan designed to repay all its obligations to American taxpayers.4 The measures include an accelerated repayment of the outstanding balance (including all accrued interest and fees) on the FRBNY revolving credit facility and termination of that facility, the acquisition of the majority of the FRBNY's preferred interests in the AIA and ALICO special purpose vehicles (SPVs) by the U.S. Treasury, and the conversion of the AIG preferred stock currently owned by the Treasury and the Credit Facility Trust into common equity of AIG. Under the plan, AIG expects to repay the revolving credit facility with parent company resources as well as with proceeds from asset dispositions currently underway, including the initial public offering of AIA and the pending sale of ALICO to MetLife, Inc.
- To facilitate the acquisition of the FRBNY's preferred interests in the AIA and ALICO SPVs by the U.S. Treasury, AIG will draw down up to $22 billion of undrawn Series F funds available to the company under the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) to purchase an equal amount of the FRBNY's preferred interests in the SPVs. Immediately thereafter, AIG will transfer these interests to the U.S. Treasury as consideration for the Series F preferred shares. AIG also will apply the proceeds of future asset dispositions, including the announced sales of the AIG Star Life Insurance Co. and AIG Edison Life Insurance, discussed below, to retire the remainder of the FRBNY's SPV preferred interests. AIG expects that it will have repaid the FRBNY in full for the revolving credit facility and preferred interests upon completion of these transactions.
- Also on September 30, 2010, AIG announced a definitive agreement to sell its Japan-based life insurance subsidiaries, AIG Star Life Insurance Co., Ltd. and AIG Edison Life Insurance Company, to Prudential Financial, Inc., for a total purchase price of $4.8 billion, comprising $4.2 billion in cash and $0.6 billion in the assumption of third-party debt. The transaction is subject to receipt of regulatory approval and is expected to close in the first quarter of 2011.
- As of September 29, 2010, the maximum principal amount of credit available under the AIG revolving credit facility was reduced from $30.0 billion to approximately $29.3 billion in connection with sales of Sun America Affordable Housing Partnership tax credits, Transatlantic Holdings, Inc. stock, and Harch CLO III Limited, Class A-1 Floating Rate Notes.
- The balance on the AIG revolving credit facility decreased by $0.5 million between August 25 and September 29, 2010, as presented in table 17A. The decline was primarily attributable to principal repayments and reductions, which outpaced principal drawdowns on the facility.
Background
On September 16, 2008, the Federal Reserve, with the full support of the Treasury Department, announced that it would lend to AIG to prevent a disorderly failure of this systemically important firm, protect the financial system and the broader economy, and provide the company time to restructure its operations in an orderly manner. Initially, the FRBNY extended an $85 billion line of credit to the company. The terms of the credit facility are disclosed on the Board's website at www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/bst_supportspecific.htm. Loans outstanding under this facility are presented weekly in table 1 of the H.4.1 statistical release and included in "Other loans" in tables 10 and 11 of the H.4.1 statistical release.
Table 17A. AIG Revolving Credit Facility
Millions of dollars
| Value | |
|---|---|
| Balance on August 25, 2010 | 19,444 |
| Principal drawdowns | 1,000 |
| Principal repayments and reductions | (1,603) |
| Recapitalized interest and fees | 17 |
| Restructuring allowance, net | 46 |
| Balance on September 29, 2010 | 18,904 |
Table 17B. Preferred Interests in AIA Aurora LLC and ALICO Holdings LLC
Millions of dollars
| Balance on September 29, 2010 | Value |
|---|---|
| Preferred Interests in AIA Aurora LLC and ALICO Holdings LLC1 | 25,733 |
| Accrued dividends on preferred interests in AIA Aurora LLC and ALICO Holdings LLC | 321 |
On November 10, 2008, the Federal Reserve and the Treasury announced a restructuring of the government's financial support to AIG. As part of this restructuring, two new limited liability companies (LLCs), Maiden Lane II LLC and Maiden Lane III LLC, were created, and the line of credit extended to AIG was reduced from $85 billion to $60 billion. (On October 8, 2008, the FRBNY was authorized to extend credit under a special securities borrowing facility to certain AIG subsidiaries. This arrangement was discontinued after the establishment of the Maiden Lane II facility.) More detail on these LLCs is reported in the remainder of this section. Additional information is included in tables 5 and 6 of the H.4.1 statistical release.
On March 2, 2009, the Federal Reserve and the Treasury announced further restructuring of the government's assistance to AIG, designed to enhance the company's capital and liquidity in order to facilitate the orderly completion of the company's global divestiture program. Additional information on the restructuring is available at www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/other/20090302a.htm.
On April 17, 2009, the FRBNY implemented a loan restructuring adjustment that was previously approved and announced on March 2, 2009. The interest rate on the loan to AIG, the three-month Libor plus 300 basis points, was modified by removing the existing interest rate floor of 3.5 percent on the Libor component. Consistent with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), as of July 29, 2009, the reported value of the AIG revolving credit extension was reduced by a $1.3 billion adjustment to reflect the loan restructuring. This restructuring adjustment is intended to recognize the economic effect of the reduced interest rate and will be recovered as the adjustment is amortized over the remaining term of the credit extension. The Federal Reserve expects that the credit extension, including interest and commitment fees under the modified terms, will be fully repaid.
The lending under this facility is secured by a pledge of assets of AIG and its primary nonregulated subsidiaries, including all or a substantial portion of AIG's ownership interest in its regulated U.S. and foreign subsidiaries. Furthermore, AIG's obligations to the FRBNY are guaranteed by certain domestic, nonregulated subsidiaries of AIG with more than $50 million in assets.
On June 25, 2009, the FRBNY entered into agreements with AIG to carry out two transactions previously approved and announced on March 2, 2009, as part of the restructuring of the U.S. government's assistance to AIG. These transactions were completed on December 1, 2009. Under these agreements, the FRBNY received preferred interests in two special purpose vehicles (SPVs), AIA Aurora LLC and ALICO Holdings LLC, formed to hold the outstanding common stock of AIG's largest foreign insurance subsidiaries, AIA Group, Limited (AIA) and American Life Insurance Company (ALICO). In exchange, upon the closing of each transaction and the resulting issuance of preferred interests, the outstanding balance of, and amount available excluding capitalized interest and fees to AIG under, the revolving credit facility was reduced by $25 billion. Specifically, the maximum amount available was reduced from $60 billion to $35 billion. By establishing the AIA and ALICO SPVs as separate legal entities, these transactions positioned AIA and ALICO for future initial public offerings (IPOs) or sale. On the H.4.1 statistical release, accrued but unpaid dividends on the preferred interests in the two SPVs are included in "Other Federal Reserve assets" in table 1, and in "Other assets" in tables 10 and 11.
On March 1, 2010, AIG announced the signing of a definitive agreement for the sale of AIA to Prudential plc (Prudential) for approximately $35.5 billion, including approximately $25 billion in cash, $8.5 billion in face value of equity and equity-linked securities, and $2.0 billion in face value of preferred stock of Prudential, subject to closing adjustments. AIG stated that the cash portion of the proceeds from the sale would be used to fully redeem the approximately $16 billion of preferred interests held by the FRBNY in the SPV that holds AIA, and to repay approximately $9 billion of its borrowing under the revolving credit facility with the FRBNY. The transaction was approved by the boards of directors of both AIG and Prudential, and was expected to close by the end of 2010, subject to approval by Prudential shareholders, regulatory approvals, and customary closing conditions.
In early June 2010, in response to efforts by Prudential to negotiate for a lower purchase price of $30.4 billion, AIG announced that it would not consider modification to the agreed-upon terms (described above) of the transaction. Subsequently, Prudential announced its intention to not proceed with the transaction. On June 3, 2010, Prudential and AIG confirmed that the parties had agreed to terminate the definitive agreement for the sale of AIA, as provided for in the sale agreement. In July 2010, AIG announced plans to conduct an initial public offering of AIA by seeking a listing of AIA on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange.
On March 8, 2010, AIG announced the signing of a definitive agreement for the sale of ALICO to MetLife, Inc. for approximately $15.5 billion, including $6.8 billion in cash and the remainder in equity securities of MetLife, subject to closing adjustments. AIG stated that the cash portion of the proceeds from this sale would be used to redeem an equivalent amount of the approximately $9 billion of preferred interests held by the FRBNY in the SPV that holds ALICO. The transaction was approved by the boards of directors of both AIG and MetLife, and is expected to close by the end of 2010, subject to the approvals of certain domestic and international regulatory bodies and to customary closing conditions. AIG has stated that it intends to monetize the securities received in the ALICO transaction over time, subject to market conditions, following the lapse of certain minimum holding periods set forth in the definitive agreement entered into with Metlife. Excess cash proceeds and proceeds from AIG's efforts to monetize the securities received in the transaction will be used to redeem any outstanding preferred interests and then to repay outstanding amounts borrowed under the revolving credit facility with the FRBNY.
Under the AIG revolving credit facility, as a general matter, all net cash proceeds received from the sale by AIG of its subsidiaries or businesses (other than sales in the ordinary course of business) must be applied to pay down outstanding borrowings under the facility (and related accrued and unpaid interest) unless otherwise waived. Additionally, the maximum amount of available credit to AIG under the revolving credit facility is reduced by the amount of net cash proceeds applied to pay the principal amount of outstanding borrowings under the facility, unless such requirement is waived by the FRBNY. Between March and September 2010, the maximum amount available under the AIG revolving credit facility was reduced from $34.4 billion to approximately $29.3 billion in connection with AIG's sale of interests in several subsidiaries. The largest payment, of approximately $3.95 billion, was made on August 20, 2010. AIG funded this payment with proceeds from the issuance of senior secured notes by International Lease Finance Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary.
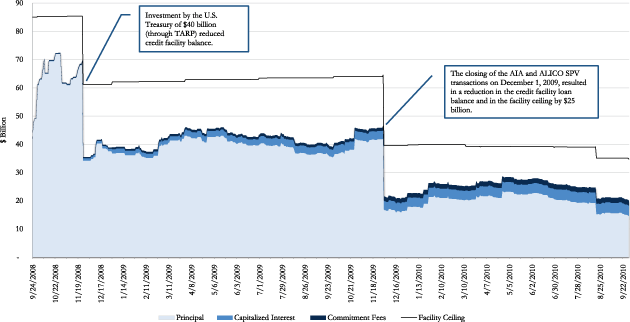
Figure 3 presents the amount of credit extended to AIG over time through the credit facility, including the principal, interest, and commitment fees, along with the facility ceiling.
Figure 3. AIG Revolving Credit
Accessible version
Maiden Lane II LLC
Pursuant to authority granted by the Federal Reserve Board under Section 13(3) of the Federal Reserve Act, the FRBNY, on December 12, 2008, lent approximately $19.5 billion to a newly formed Delaware limited liability company, Maiden Lane II LLC, to partially fund the purchase of residential mortgage-backed securities (RMBS) from the securities lending portfolio of several regulated U.S. insurance subsidiaries of AIG. Maiden Lane II LLC acquired the RMBS, which had an aggregate par value of approximately $39.3 billion, at the then-current market value of the RMBS of approximately $20.8 billion, which was substantially below par value.5 The full portfolio of RMBS held by Maiden Lane II LLC serves as collateral for the Federal Reserve's loan to Maiden Lane II LLC. AIG's insurance subsidiaries also have a $1 billion subordinated position in Maiden Lane II LLC that is available to absorb first any losses that may be realized.
The net portfolio holdings of Maiden Lane II LLC are presented in tables 1, 10, and 11 of the weekly H.4.1 statistical release. Additional detail on the accounts of Maiden Lane II LLC is presented in table 5 of the H.4.1 statistical release. Details on the terms of the loan, as well as information on the holdings of the Maiden Lane II LLC, including the CUSIP number, descriptor, and the current principal balance or notional amount outstanding for all the positions in the portfolio, is published on the FRBNY website at www.newyorkfed.org/markets/maidenlane2.html.
Information about the assets and liabilities of Maiden Lane II LLC is presented as of June 30, 2010, in tables 18 through 20 and figure 4. This information is updated on a quarterly basis.
Table 18. Maiden Lane II LLC Outstanding Principal Balance of Senior Loan and Fixed Deferred Purchase Price
Millions of dollars
| FRBNY senior loan | AIG fixed deferred purchase price | |
|---|---|---|
| Principal balance at closing | 19,494 | 1,000 |
| Most Recent Quarterly Activity | ||
| Principal balance on 3/31/2010 (including accrued and capitalized interest) | 15,283 | 1,045 |
| Accrued and capitalized interest 3/31/2010 to 6/30/2010 | 48 | 9 |
| Repayment during the period from 3/31/2010 to 6/30/2010 | (660) | _ |
| Principal balance on 6/30/2010 (including accrued and capitalized interest) | 14,672 | 1,053 |
Table 19. Maiden Lane II LLC Summary of RMBS Portfolio Composition, Cash and Cash Equivalents, and Other Assets and Liabilities
Millions of dollars
| Fair value on 6/30/2010 | Fair value on 3/31/2010 | |
|---|---|---|
| Alt-A ARM | 4,957 | 4,934 |
| Subprime | 8,781 | 8,791 |
| Option ARM | 1,089 | 1,032 |
| Other1 | 1,264 | 1,225 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | 230 | 220 |
| Other assets2 | 4 | 3 |
| Other liabilites3 | (1) | (7) |
| Net assets | 16,323 | 16,198 |
1. Includes all asset sectors that, individually, represent less than 5 percent of aggregate outstanding fair value of securities in the portfolio. Return to table
2. Including interest and principal receivable and other receivables. Return to table
3. Including accrued expenses and other payables. Return to table
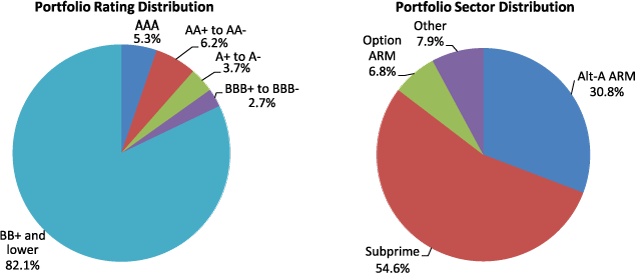
Table 20. Maiden Lane II LLC Securities Distribution by Sector and Rating
Percent, as of June 30, 2010
| RMBS sector | Rating | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAA | AA+ to AA- | A+ to A- | BBB+ to BBB- | BB+ and lower | Total | |
| Alt-A ARM | 0.4 | 2.8 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 24.9 | 30.8 |
| Subprime | 4.9 | 2.9 | 2.2 | 1.3 | 43.3 | 54.6 |
| Option ARM | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 6.7 | 6.8 |
| Other1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 7.2 | 7.9 |
| Total | 5.3 | 6.2 | 3.7 | 2.7 | 82.1 | 100.00 |
1. Includes all asset sectors that, individually, represent less than 5 percent of the aggregate fair value of securities in the portfolio. Return to table
Figure 4. Maiden Lane II LLC Securities Distribution as of June 30, 2010
Maiden Lane III LLC
Pursuant to authority granted by the Federal Reserve Board under Section 13(3) of the Federal Reserve Act, the FRBNY in November and December 2008, lent approximately $24.3 billion to a newly formed Delaware limited liability company, Maiden Lane III LLC, to fund the purchase of certain asset-backed collateralized debt obligations (ABS CDOs) from certain counterparties of AIG Financial Products Corp. (AIGFP) on which AIGFP had written credit default swaps and similar contracts. Maiden Lane III LLC acquired these CDOs, which had an aggregate par value of approximately $62.1 billion, at the then-current market value of the CDOs of approximately $29.6 billion, which was substantially below par value.6 The full portfolio of CDOs held by Maiden Lane III LLC serves as collateral for the Federal Reserve's loan to Maiden Lane III LLC. An AIG subsidiary also has a $5 billion subordinated position in Maiden Lane III LLC that is available to absorb first any losses that may be realized. Assets of the portfolio of the LLC will be managed to maximize cash flows to ensure repayment of obligations of the LLC while minimizing disruptions to financial markets.
The net portfolio holdings of Maiden Lane III LLC are presented in tables 1, 10, and 11 of the weekly H.4.1 statistical release. Additional detail on the accounts of Maiden Lane III LLC is presented in table 6 of the H.4.1 statistical release. Information on the holdings of the Maiden Lane III LLC, including the CUSIP number, descriptor, and the current principal balance or notional amount outstanding for all the positions in the portfolio, is published on the FRBNY website at www.newyorkfed.org/markets/maidenlane3.html.
Information about the assets and liabilities of Maiden Lane III LLC is presented as of June 30, 2010, in tables 21 through 23 and figure 5. This information is updated on a quarterly basis.
Table 21. Maiden Lane III LLC Outstanding Principal Balance of Senior Loan and Equity Contribution
Millions of dollars
| FRBNY senior loan | AIG equity contribution | |
|---|---|---|
| Principal balance at closing | 24,339 | 5,000 |
| Most Recent Quarterly Activity | ||
| Principal balance on 3/31/2010 (including accrued and capitalized interest) | 17,324 | 5,235 |
| Accrued and capitalized interest to 3/31/2010 to 6/30/2010 | 54 | 43 |
| Repayment during the period from 3/31/2010 to 6/30/2010 | (1,083) | _ |
| Principal balance on 6/30/2010 (including accrued and capitalized interest) | 16,294 | 5,278 |
Table 22. Maiden Lane III LLC Summary of Portfolio Composition, Cash and Cash Equivalents, and Other Assets and Liabilities
Millions of dollars
| Fair value on 6/30/2010 | Fair value on 3/31/2010 | |
|---|---|---|
| High-Grade ABS CDO | 15,500 | 15,437 |
| Mezzanine ABS CDO | 1,997 | 2,098 |
| Commercial real estate CDO | 5,564 | 5,517 |
| RMBS, CMBS, & Other | 266 | 269 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | 390 | 354 |
| Other assets1 | 32 | 28 |
| Other liabilites2 | (3) | (5) |
| Total | 23,747 | 23,699 |
1. Including interest and principal receivable and other receivables. Return to table
2. Including accrued expenses. Return to table
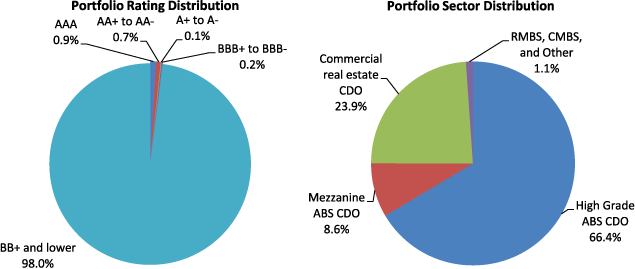
Table 23. Maiden Lane III LLC Securities Distribution by Sector, Vintage, and Rating
Percent, as of June 30, 2010
| Sector and vintage1 | Rating | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAA | AA+ to AA- | A+ to A- | BBB+ to BBB- | BB+ and lower | Total | |
| High-grade ABS CDO | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 66.4 | 66.4 |
| Pre-2005 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 22.8 | 22.8 |
| 2005 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 30.2 | 30.2 |
| 2006 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.7 | 6.7 |
| 2007 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.8 | 6.8 |
| Mezzanine ABS CDO | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 8.4 | 8.6 |
| Pre-2005 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 5.1 | 5.2 |
| 2005 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.7 | 2.7 |
| 2006 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2007 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Commercial real-estate CDO | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 22.4 | 23.9 |
| Pre-2005 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.1 | 4.5 |
| 2005 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2006 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2007 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 19.4 | 19.4 |
| RMBS, CMBS, and Other | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 1.1 |
| Pre-2005 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| 2005 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.9 |
| 2006 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 2007 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Total | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 98.0 | 100.0 |
1. The year of issuance with the highest concentration of underlying assets as measured by outstanding principal balance determines the vintage of the CDO. Return to table
Figure 5. Maiden Lane III LLC Securities Distribution as of June 30, 2010
5. The aggregate amount of interest and principal proceeds from RMBS received after the announcement date, but prior to the settlement date, net of financing costs, amounted to approximately $0.3 billion and therefore reduced the amount of funding required at settlement by $0.3 billion, from $20.8 billion to $20.5 billion. Return to text
6. The aggregate amount of interest and principal proceeds from CDOs received after the announcement date, but prior to the settlement dates, net of financing costs, amounted to approximately $0.3 billion and therefore reduced the amount of funding required at settlement by $0.3 billion, from $29.6 billion to $29.3 billion. Return to text


