Annual Report 2013
The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, is a federal system composed of a central governmental agency--the Board of Governors--and 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks.
The Board of Governors, located in Washington, D.C., consists of seven members appointed by the President of the United States and supported by a 2,648-person staff. Besides conducting research, analysis, and policymaking related to domestic and international financial and economic matters, the Board plays a major role in the supervision and regulation of U.S. financial institutions and activities, has broad oversight responsibility for the nation's payments system and the operations and activities of the Federal Reserve Banks, and plays an important role in promoting consumer protection, fair lending, and community development.
About This Report
This report covers Board and System operations and activities during calendar-year 2013. The report includes the following sections:
- Monetary policy and economic developments. Section 2 provides adapted versions of the Board's semiannual monetary policy reports to Congress.
- Federal Reserve operations. Section 3 provides a summary of Board and System activities in the areas of supervision and regulation; section 4, in consumer and community affairs; and section 5, in Reserve Bank operations.
- Dodd-Frank Act implementation and other requirements. Section 6 summarizes the Board's efforts in 2013 to implement provisions of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act as well as the Board's compliance with the Government Performance and Results Act of 1993.
- Policy actions and litigation. Section 7 and section 8 provide accounts of policy actions taken by the Board in 2013, including new or amended rules and regulations and other actions as well as the deliberations and decisions of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC); section 9 summarizes litigation involving the Board.1
- Statistical tables. Section 10 includes 14 statistical tables that provide updated historical data concerning Board and System operations and activities.
- Federal Reserve System audits. Section 11 provides detailed information on the several levels of audit and review conducted in regards to System operations and activities, including those provided by outside auditors and the Board's Office of Inspector General.
- Federal Reserve System budgets. Section 12 presents information on the 2013 budget performance of the Board and Reserve Banks, as well as their 2014 budgets, budgeting processes, and trends in their expenses and employment.
- Federal Reserve System organization. Section 13 provides listings of key officials at the Board and in the Federal Reserve System, including the Board of Governors, its officers, FOMC members, several System councils, and Federal Reserve Bank and Branch officers and directors.
For More Background on Board Operations
For more information about the Federal Reserve Board and the Federal Reserve System, visit the Board's website at www.federalreserve.gov/aboutthefed/default.htm. An online version of this Annual Report is available at www.federalreserve.gov/pubs/alpha.htm.
Return to textAbout the Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System, which serves as the nation's central bank, was created by an act of Congress on December 23, 1913. The System consists of a seven-member Board of Governors with headquarters in Washington, D.C., and the 12 Reserve Banks located in major cities throughout the United States.
The Federal Reserve Banks are the operating arms of the central banking system, carrying out a variety of System functions, including operating a nationwide payment system; distributing the nation's currency and coin; under authority delegated by the Board of Governors, supervising and regulating a variety of financial institutions and activities; serving as fiscal agents of the U.S. Treasury; and providing a variety of financial services for the Treasury, other government agencies, and other fiscal principals.
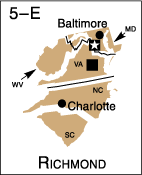
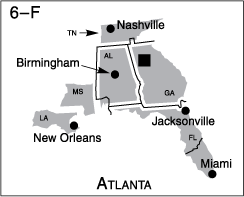
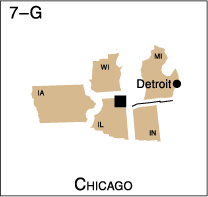
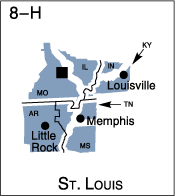
The following maps identify Federal Reserve Districts by their official number, city, and letter designation.
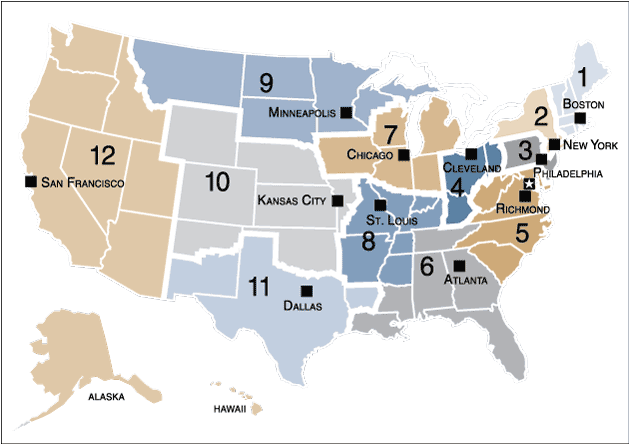
Accessible Version
![]() Federal Reserve Bank city
Federal Reserve Bank city
![]() Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Washington, D.C.
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Washington, D.C.
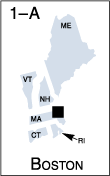 Accessible Version
Accessible Version
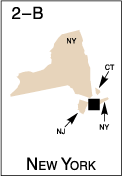 Accessible Version
Accessible Version
 Accessible Version
Accessible Version
 Accessible Version
Accessible Version
 Accessible Version
Accessible Version
 Accessible Version
Accessible Version
 Accessible Version
Accessible Version
 Accessible Version
Accessible Version
 Accessible Version
Accessible Version
 Accessible Version
Accessible Version
 Accessible Version
Accessible Version
 Accessible Version
Accessible Version
![]() Federal Reserve Bank city
Federal Reserve Bank city
![]() Federal Reserve Branch city
Federal Reserve Branch city
![]() Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Washington, D.C.
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Washington, D.C.
![]() Branch boundary
Branch boundary
References
1. For more information on the FOMC, see the Board's website at www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomc.htm. Return to text
